CAIRS
Understanding Vision Changes After CAIRS KeraNatural Treatment in Keratoconus
Factors Influencing Vision Change:
1. Corneal Thickness:
Corneal thickness plays a pivotal role in determining the success of CAIRS KeraNatural treatment. Thinner corneas may pose challenges in achieving optimal visual outcomes, while adequate thickness facilitates proper tissue integration and visual improvement.
2. Age:
Age influences corneal healing response and visual recovery post-treatment. Younger patients may experience more favorable outcomes due to enhanced healing capacity and corneal biomechanical properties compared to older individuals.
3. Previous Crosslinking Treatment:
Patients with a history of corneal crosslinking may exhibit altered corneal biomechanics and healing responses, affecting the efficacy of CAIRS KeraNatural treatment. Close monitoring and individualized management are crucial in such cases.
4. Corneal Biomechanic Properties:
Variations in corneal biomechanical properties, such as elasticity and rigidity, influence tissue integration and visual outcomes post-treatment. Patient-specific biomechanical assessments aid in predicting treatment success and optimizing visual correction.
5. Dry Eye:
Pre-existing dry eye conditions can hinder corneal healing and visual recovery following CAIRS KeraNatural treatment. Adequate preoperative management of dry eye symptoms and postoperative monitoring are essential for optimal outcomes.

Understanding Vision Changes:
1. Potential for Vision Improvement:
CAIRS KeraNatural treatment holds significant potential for enhancing visual acuity in keratoconus patients. By restoring corneal integrity and regularizing the refractive surface, patients may experience substantial vision improvement post-treatment.
2. Individualized Response:
Each keratoconus case presents unique challenges and treatment responses. Factors such as corneal morphology, patient age, ocular health, and treatment history contribute to individualized vision changes post-CAIRS KeraNatural treatment.
3. Absence of Vision Loss:
Importantly, CAIRS KeraNatural treatment is not associated with vision loss in keratoconus patients. While individual outcomes may vary, the treatment aims to stabilize or enhance visual acuity without compromising existing vision.
Conclusion:
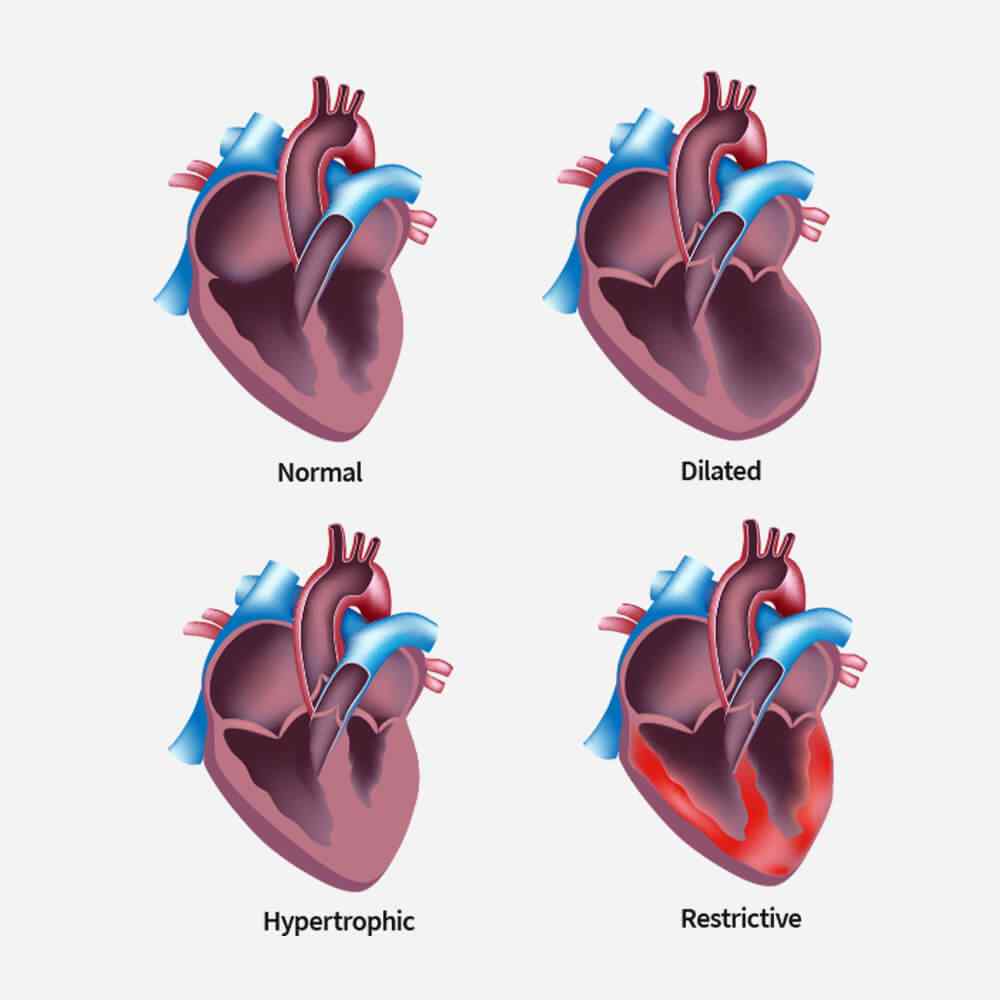
Types of Cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is a condition where your ventricles do not thicken, yet they still become stiff and rigid and cannot pump blood effectively.
In this type of cardiomyopathy, the pumping ability of your heart’s main pumping chamber — the left ventricle — becomes enlarged (dilated) and can’t effectively pump blood out of the heart.
This type involves abnormal thickening of your heart muscle, which makes it harder for the heart to work. It mostly affects the muscle of your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle).
In this rare type of cardiomyopathy, the muscle in the lower right heart chamber (right ventricle) is replaced by scar tissue, which can lead to heart rhythm problems. It’s often caused by genetic mutations.
Related TreatmentAngioplasty
Angioplasty uses a tiny balloon catheter that is inserted in a blocked blood vessel to help widen it and improve blood flow to your heart. Angioplasty is often combined with the placement of a small wire mesh tube called a stent. The stent helps prop the artery open, decreasing its chance of narrowing again.